- Home
- Technology
- What is Cloud Computing ? Defi ...
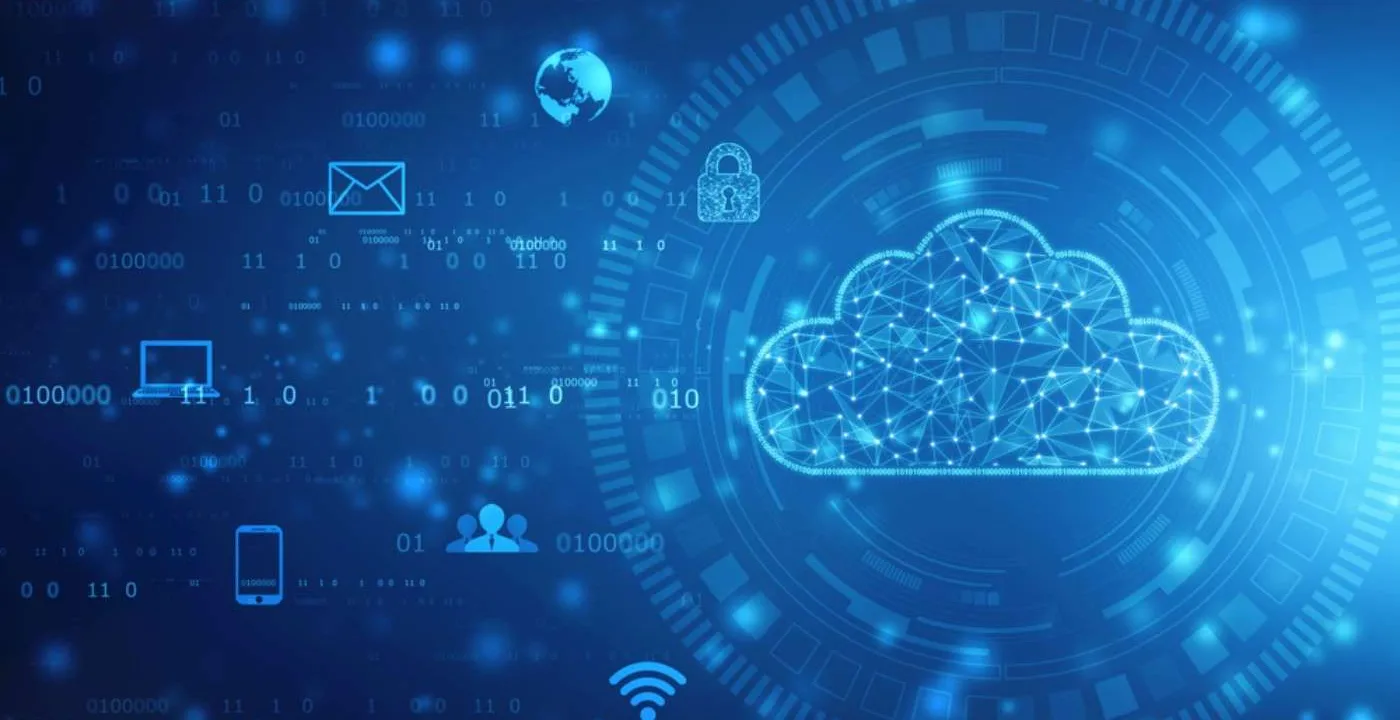
Cloud computing is defined as the use of hosted services, such as data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software over the internet. Since cloud computing began, the world has seen an explosion of cloud-based applications and services in IT, which continue to expand. In 2024, almost every small and large application we use resides on the cloud, helping us save storage space, expenses, and time.
Table Of Content
- What is Cloud Computing ?
- Benefits of cloud computing.
- Types of Cloud Computing ?
What is Cloud Computing ?
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing. Instead of buying, owning, and maintaining physical data centers and servers, you can access technology services, such as computing power, storage, and databases, on an as-needed basis from a cloud provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS).
In Cloud computing we can host services, such as data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software over the internet. The data is stored on physical servers, which are maintained by a cloud service provider. Computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, are available on-demand, without direct management by the user in cloud computing.
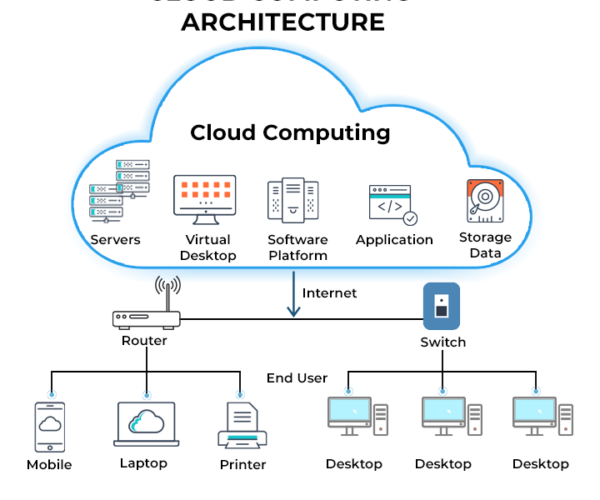
Instead of storing files on a storage device or hard drive, a user can save them on cloud, making it possible to access the files from anywhere, as long as they have access to the web.
Based on the deployment model, cloud can also be classified as public, private, and hybrid cloud.
Types of cloud computing
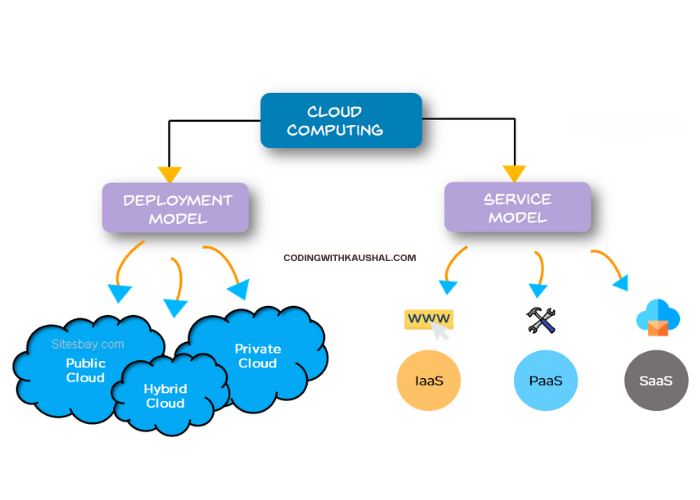
Cloud computing can either be classified based on the deployment model or the type of service.
Based on the specific deployment model, we can classify cloud as
- Public
- Private
- Hybrid
And based on Services, it can be classified as
- Infrastructure-as-a-service(IaaS)
- Platform-as-a-service(PaaS)
- Software-as-a-service(SaaS)
Who is using Cloud Computing ?
Organizations of every type, size, and industry are using the cloud for a wide variety of use cases, such as data backup, disaster recovery, email, virtual desktops, software development and testing, big data analytics, and customer-facing web applications. For example, healthcare companies are using the cloud to develop more personalized treatments for patients. Financial services companies are using the cloud to power real-time fraud detection and prevention. And video game makers are using the cloud to deliver online games to millions of players around the world.
Key Benefits of cloud computing
The most important reason why cloud computing is growing rapidly is the various benefits it offers. It saves the time and resources required to set up full-fledged physical IT infrastructure. Let’s have look at all the benefits cloud offers:
Reduced costs: Maintaining IT systems requires big amount of capital, something that cloud helps reduce. By using the resources provided by the cloud provider, businesses avoid the need to purchase expensive infrastructure, substantially reducing their expenditure. Cloud providers work on the pay-as-you-go model, which means businesses only pay for the services they use, further reducing costs.
Scalability: Cloud allows organizations to grow their users from merely a few to thousands in a very short time. Depending on the need, a business can scale their storage needs up or down, allowing organizations to be flexible.
Elasticity: With cloud computing, you don’t have to over-provision resources up front to handle peak levels of business activity in the future. Instead, you provision the amount of resources that you actually need. You can scale these resources up or down to instantly grow and shrink capacity as your business needs change.
Flexibility and collaboration: Since the data on cloud can be accessed directly via the internet, it gives employees the ability to work from anywhere, anytime. Cloud gives you the freedom to set up your virtual office anywhere you are. It also allows teams to work on a project across locations by giving them access to the same files as third-party vendors.
Agility: The cloud gives you easy access to a broad range of technologies so that you can innovate faster and build nearly anything that you can imagine. You can quickly spin up resources as you need them–from infrastructure services, such as compute, storage, and databases, to Internet of Things, machine learning, data lakes and analytics, and much more.
Recent Post
Page Titile Example Post25
- May 15, 2025
- 1 min read
Page Titile Example Post26
- May 15, 2025
- 1 min read
Page Titile Example Post27
- May 15, 2025
- 1 min read